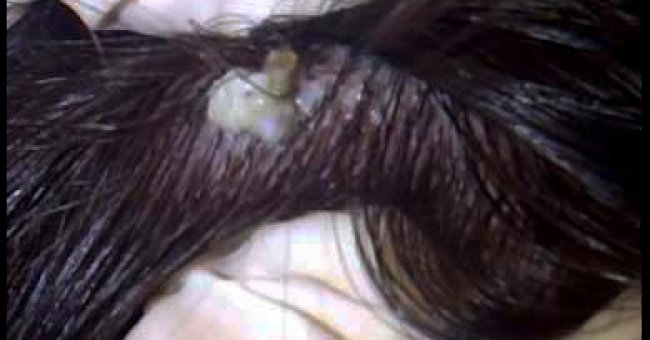
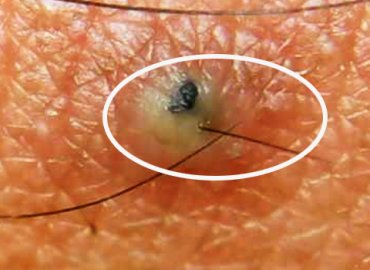
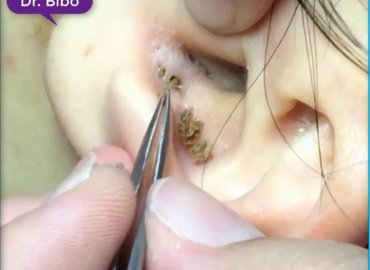
Blackheads are small bumps that appear on your skin due to clogged hair follicles. These bumps are called blackheads because the surface looks dark or black. Blackheads are a mild type of acne that usually form on the face, but they can also appear on the following body parts: back.
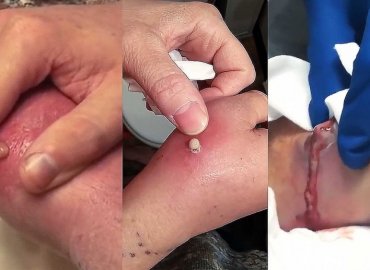
Blackheads are pores that have been partially blocked by oil, dead skin cells and bacteria. … Blackheads often take a long time to clear and it may be tempting to squeeze to clear them faster. However, many experts recommend against squeezing and suggest other ways of clearing blackheads.
Cysts are fluid-filled pockets that form on the skin. While not usually dangerous, they can be painful and annoying. Depending on the type of cyst, you can usually have a cyst medically removed with the assistance of a doctor.
Dealing with Facial Cysts
Decide if medical intervention is necessary. Facial cysts, medically referred to as sebaceous cysts, can be annoying and unsightly but they don’t necessarily require medical intervention. If the cyst is not painful, it might be best to leave it alone to avoid complications having it removed. However, you should see a doctor if any of the following develop:
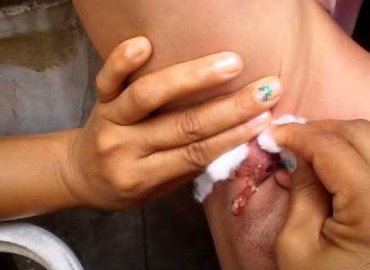
-Facial cysts are usually small, round lumps just underneath the skin. They may be black, reddish or yellowish, and occasionally release foul-smelling discharge. Cysts are generally more painful than other skin conditions, such as pimples.
-If the cyst ruptures, this can lead to a potentially dangerous boil-like infection. Prompt treatment and removal is required.
-If the cyst suddenly becomes painful and swollen, it may be infected. See a doctor to get the cyst removed and get the proper antibiotics.
-In very rare cases, a cyst can lead to skin cancer. During your regular annual doctor’s exam, ask your doctor to look at the cyst and determine if it poses a risk for cancer.
Dealing with Facial Cysts
Ask your doctor for an injection. If the cyst is infected or painful, your doctor can inject the cyst with a medication. While this will not fully remove the cyst, it will reduce redness and swelling. This can make the cyst less noticeable.
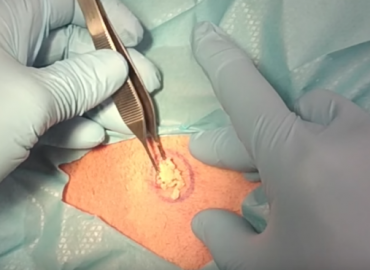
Have the cyst drained. If the cyst grows significantly or becomes painful and uncomfortable, you can have it medically removed. The cyst can be cut open and drained by your doctor.
– The doctor will make a small cut in the cyst and gently drains out the built up fluid. The procedure is fairly quick and usually not painful.
– The major downside to this method is that cysts often reoccur after being lanced and drained.
Ask about surgery. The only way to fully remove a cyst is through surgery. Talk to your doctor about undergoing surgery if you want a cyst removed.
– Cyst removal surgery is minor. It does not take very long and recovery time is relatively brief. However, you may have to return to your doctor’s office after the surgery to remove any stitches.
– Surgery is very safe and usually prevents cysts from occurring. However, cysts do not
Squeezing and popping blackheads is a bad idea and not the correct way to remove blackheads. You can’t really pop a blackhead to remove it, because the oil is too tightly stuck in your skin and if you try anyway you will cause trauma to the skin around the blackhead leaving it red and irritated.
Distinguish between cysts in the breast and tumors. Cysts can be in one or both breasts. Without a mammogram or needle biopsy it is almost impossible to distinguish between the two different types of lumps in the breast. Symptoms of a breast cyst will include:
- Smooth, easily movable lump with distinct edges
- Pain or tenderness over the lump
- Size and tenderness will increase just before your period starts
- Size and tenderness will decrease when your period ends
Understand cystic acne. Acne is a general term that describes a variety of different types of pimples, blackheads, pustules, whiteheads and cysts. Cystic acne are nodules that are red, raised, often 2–4 mm in size and nodular and are the most severe form of acne. The infection in a cystic acne is deeper than that in other pustules or whiteheads. Cystic acne is painful.
Identify a ganglion cyst. These are the most common types of lumps found on the hand and wrist. They are not cancerous and often harmless. Filled with fluid, they can quickly appear, disappear or change in size. They do not require treatment unless they interfere with function or are unacceptable in appearance.
Determine if pain is from a pilonidal cyst. In this condition there is a cyst, abscess or dimple that forms in the crease between the buttocks that runs from the lower end of the spine to the anus. It can be caused from wearing tight clothing, excess body hair, sitting for long periods of time or obesity. Symptoms can include pus from the area, tenderness over the cyst, or the skin may be warm, tender or swollen near the tailbone. Or there may not be any symptoms beside a pit or dimple at the base of the spine.
Distinguish a Bartholin gland cyst. These glands are located on either side of the vaginal opening to lubricate the vagina. When the gland becomes obstructed, a relatively painless swelling forms called a Bartholin’s cyst. If the cyst is not infected you may not notice it. An infection can occur in a matter of days causing tenderness, fever, discomfort walking, pain with intercourse, and a tender, painful lump near the vaginal opening.
See a doctor for swelling in the testicles. All testicular swelling must be diagnosed by a physician to determine the differences between a cyst, cancerous growth, hydrocele or infection in the testicles. A testicular cysts, also called a spermatocele or epididymal cyst, is typically a painless, fluid-filled, noncancerous sac in the scrotum above the testicles. T
Consider getting a second opinion if you are not satisfied with your physician’s diagnosis and treatment. Although most epidermoid and pilar cysts do not require treatment from a physician, if you do seek medical advice and are not satisfied with the results seek a second opinion. Most sebaceous and epidermoid cysts are straightforward, but there are other conditions that may mimic these cysts.
In a case study written in the Royal College of Surgeons of England, the authors presented two cases in which melanoma and a deep oral cavity were originally mistaken for a sebaceous cyst.
There are a variety of other infectious processes that may be mistaken for a sebaceous cyst, including boils, furuncles and carbuncles.
Treating a Cyst at Home
Tret uninfected epidermoid and sebaceous cysts at home. Signs of infection include the area becoming swollen, red, tender, or red and warm. If your home treatment for these cysts is not effective or if you experience symptoms, which indicate an infection, you should seek medical care from your physician.
If the cyst causes pain or discomfort with walking or intercourse, medical care is needed to treat the cyst.
Use a wet, warm compress over an epidermoid cyst to encourage it to drain and heal. The washcloth should be hot but not so hot that it burns the skin. Place it over the cyst two to three times a day.
Cystic acne responds better to ice than it does to heat.
Bartholin gland cysts can be treated at home using warm water