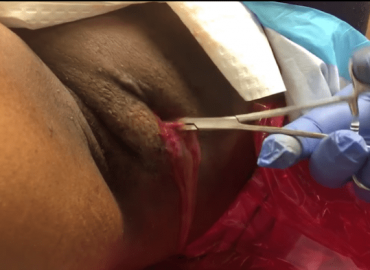
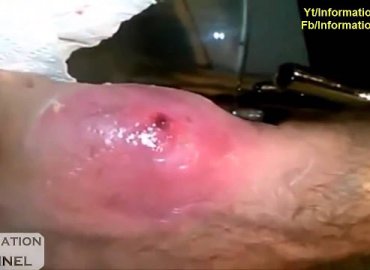
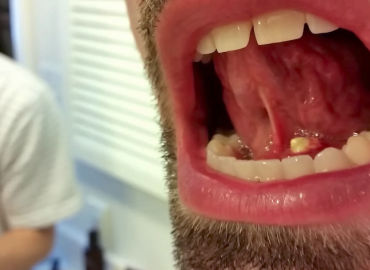
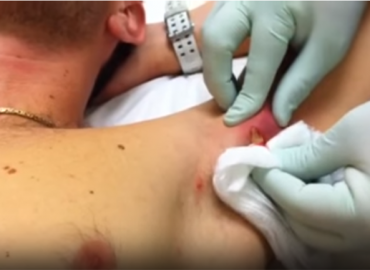
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection.An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis is known as a pustule, pimple, or spot.
Pus consists of a thin, protein-rich fluid, known as liquor puris, and dead leukocytes from the body’s immune response (mostly neutrophils).During infection, macrophages release cytokines which trigger neutrophils to seek the site of infection by chemotaxis. There, the neutrophils release granules which destroy the bacteria. The bacteria resist the immune response by releasing toxins called leukocidins.As the neutrophils die off from toxins and old age, they are destroyed by macrophages, forming the viscous pus.
Bacteria that cause pus are called pyogenic.
Although pus is normally of a whitish-yellow hue, changes in the color can be observed under certain circumstances. Pus is sometimes green because of the presence of myeloperoxidase, an intensely green antibacterial protein produced by some types of white blood cells. Green, foul-smelling pus is found in certain infections of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The greenish color is a result of the bacterial pigment pyocyanin that it produces. Amoebic abscesses of the liver produce brownish pus, which is described as looking like “anchovy paste”. Pus from anaerobic infections can more often have a foul odor.
In almost all cases when there is a collection of pus in the body, the clinician will try to create an opening to drain it. This principle has been distilled into the famous Latin aphorism “Ubi pus, ibi evacua” (“Where there is pus, evacuate it”).
Some disease processes caused by pyogenic infections are impetigo, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, and necrotizing fasciitis.
Pyogenic bacteria
- A great many species of bacteria may be involved in the production of pus. The most commonly found include:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Escherichia coli (Bacillus coli communis)
- Streptococcus pneumoniae (Fraenkel’s pneumococcus)
- Klebsiella pneumoniae (Friedländer’s bacillus)
- Salmonella typhi (Bacillus typhosus)
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Actinomyces
- Burkholderia mallei (Glanders bacillus)
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tubercle bacillus)
- Staphylococcus aureus bacteria is the most common cause of boils.
Historical terminology
In the pre-asepsis era, surgeon Frederick Treves (1853–1923) wrote, “Practically all major wounds suppurated. Pus was the most common subject of converse, because it was the most prominent feature in the surgeon’s work. It was classified according to degrees of vileness.” But pus of the right kind was considered desirable.”If a patient was lucky … a thick cream-colored odorless fluid would appear within five or six days”; such “laudable” pus was considered “a sure sign that the wound would heal” because it meant “Nature has put up a bold fight against the invader”.”On the other hand, if the pus gradually became watery, blood tinged and foul smelling, it was designated ‘sanious’ [or ‘ill-conditioned’ ] [12] and the wound condition was considered unfavorable”.[11] It later came to be understood that “laudable” pus generally implied an invasion of relatively benign staphylococcus, while “ill-conditioned” pus usually meant the more dangerous streptococcus was present.
Determining Whether a Pimple Can Be Popped
Pop whitehead pimples. Whitehead pimples have usually been around for a few days, and they have a white tip where pus has collected underneath the skin. These pimples are easy to pop, and when treated with care they can be safely removed without spreading the infection or causing scarring.
Don’t pop new pimples. Pimples that have just appeared in the past day or two aren’t ready to pop yet. Wait until the whitehead appears at the tip of the blemish.
Don’t pop pimples that are big, red, or sore. This could worsen your pimple by sending bacteria deeper into your skin. Popping a pimple this big will almost definitely lead to a scar. Only a pimple with white pus is ready to pop.
Visit a dermatologist. Dermatologists can determine the best way to treat your acne. They can prescribe creams that will eliminate your pimples. There are also several procedures they can perform that can treat severe breakouts.
The most commonly prescribed dermatologist treatment is a topical cream, rubbed on the pimples, that will remove oil from the skin and kill acne-causing bacteria.
For red, swollen pimples an oral antibiotic, hormonal birth control, or isotretinoin might be prescribed.
Large acne cysts can be removed by dermatologists through drainage and extraction, in which they remove the cyst and drain out the pus.